Money
#money #business #entrepreneur #success #motivation #bitcoin #love #cash #investment #wealth #finance #investing #trading #luxury #rich #millionaire #invest #lifestyle #cryptocurrency #financialfreedom #life #follow #entrepreneurship #marketing #instagood #crypto
Other KMN Financial Literacy pages:
HISTORY OF MONEY
The History of Money Explained in One Infographic
Published 3 years ago on January 30, 2017
By Jeff Desjardins
|
The History of Money Explained in One Infographic
Today’s infographic from Mint.com highlights the history of money, including the many monetary experiments that have taken place since ancient times. Some innovations have stood the test of time – precious metals, for example, have been used for thousands of years. Paper money and banknotes are also widespread in use, after first being turned to in China in 806 after a copper shortage prevented the minting of new coins. Other experiments didn’t have much staying power. The adoption of strange currencies such as squirrel pelts... |
Online Resources:
History of money - Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › History_of_money
The history of money concerns the development of social systems that provide at least one of the functions of money. Such systems can be understood as means ...Category:History of money · Barter · Shekel
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › History_of_money
The history of money concerns the development of social systems that provide at least one of the functions of money. Such systems can be understood as means ...Category:History of money · Barter · Shekel
The History of Money | NOVA | PBS
www.pbs.org › wgbh › nova › article › history-money
Oct 25, 1996 - 1000 B.C.: First Metal Money and Coins. Bronze and Copper cowrie imitations were manufactured by China at the end of the Stone Age and ...
www.pbs.org › wgbh › nova › article › history-money
Oct 25, 1996 - 1000 B.C.: First Metal Money and Coins. Bronze and Copper cowrie imitations were manufactured by China at the end of the Stone Age and ...
The History of Money: From Barter to Banknotes - Investopedia
www.investopedia.com › Economy › Economics
The Chinese were the first to devise a system of paper money, in approximately 770 B.C.. Money is valuable ...
www.investopedia.com › Economy › Economics
The Chinese were the first to devise a system of paper money, in approximately 770 B.C.. Money is valuable ...
YouTube Resources:
Econ Vids for Kids: What is Money?
What is money? We explore how money originates out of a barter system and the five characteristics of money: divisibility, portability, durability, recognizability, and scarcity. http://inkwellscholars.org
TED-Ed: What gives a dollar bill its value? - Doug LevinsonView full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-gives-...
The value of money is determined by how much (or how little) of it is in circulation. But who makes that decision, and how does their choice affect the economy at large? Doug Levinson takes a trip into the United States Federal Reserve, examining how the people who work there aim to balance the value of the dollar to prevent inflation or deflation. Lesson by Doug Levinson, animation by Qa'ed Mai. The History of Money: An OverviewKenneth R. Calvert, Headmaster of Hillsdale Academy and Associate Professor of History at Hillsdale College
|
History of U.S. Currency | History is Our Story | J.P. Morgan
jpmorgan
American money has changed drastically since the birth of the nation. In Part 1 of this two-part series, discover the origins of bank notes and how institutions, including one of our predecessors, played a role in creating modern money. The History of U.S. MoneySF Fed EconEd
Money hasn't always looked like it does today, but evolved over the last few centuries to become the size and shape that we now carry in our wallets. Learn how our country's vibrant history -- from times of financial crisis and war, to the demand for a stable monetary system -- transformed the appearance of American currency as we know it. Discover the role the Federal Reserve played, and continues to play, in this rich history. After watching the video, explore the SF Fed's American Currency Exhibit online, a truly priceless collection that brings history alive and shows you how currency actually shaped our country's history: http://www.frbsf.org/currency/index.html History of the US DollarIG Bank
Discover the history of the US dollar – including its origins, and the events that led to it becoming the most traded currency on the planet. |
Book Resources:
The History of Money
|
Money: The Unauthorized Biography--From Coinage to Cryptocurrencies
|
The Ascent of Money: A Financial History of the World: 10th Anniversary Edition
|
Lesson Plan Resources:
www.moneyinstructor.com › history
HISTORY LESSONS AND LESSON PLANS. The Great Depression. Students will understand the events preceding the Great Depression, and learn about "Black ...
HISTORY LESSONS AND LESSON PLANS. The Great Depression. Students will understand the events preceding the Great Depression, and learn about "Black ...
www.usmint.gov › learn › educators › a-world-of-money
Learn · For Kids · For Educators · Coin & Medal Programs · Collecting Basics · History · Artists · U.S. Mint/; Lesson Plans/; A World of Money ...
Learn · For Kids · For Educators · Coin & Medal Programs · Collecting Basics · History · Artists · U.S. Mint/; Lesson Plans/; A World of Money ...
www.tdbank.com › wowzone › lessons › Gr2-3Lesson1
PDF
INTRODUCTION TO MONEY: ORIGIN, HISTORY AND FUNCTIONS ... This lesson introduces students to types of money (cash, coin) and the ... Connections – (Students will) Recognize and use connections among mathematical ideas.
INTRODUCTION TO MONEY: ORIGIN, HISTORY AND FUNCTIONS ... This lesson introduces students to types of money (cash, coin) and the ... Connections – (Students will) Recognize and use connections among mathematical ideas.
https://www.hardmoneyhistory.com
Become a better investor by studying the history of money. Protect your portfolio and prosper by understanding the importance of hard money.
Become a better investor by studying the history of money. Protect your portfolio and prosper by understanding the importance of hard money.
A National Bank?
|
The President, Directors and Company of the Bank of the United States, commonly known as the First Bank of the United States, was a national bank, chartered for a term of twenty years, by the United States Congress on February 25, 1791. It followed the Bank of North America, the nation's first de facto national bank.
First Bank of the United States - Wikipedia Alexander Hamilton's grand experiment in central banking began in 1791 to assist a post-Revolutionary War economy and ended 20 years later. This 1830s painting ...
Hamilton argued that a national bank is “a political machine, of the greatest importance to the state.” He asserted that a national bank would facilitate ...
On December 15, 1790, Hamilton submitted a report to Congress making the case. He proposed a Bank of the United States with a $10 million capital (then five ...
High on Hamilton's list of proposals in 1780 was the creation of a national bank. The inspiration for this idea came from Great Britain. One critical element in ...
As the Republic's first Treasury secretary, Hamilton championed the idea of a national bank, proposing its establishment to Congress and convincing President ...
Why a National Bank
Treasury Secretary Alexander Hamilton creates a Bank of the United States, modeled after the Bank of England, where all federal deposits are held.
|
US Economic History 3 — National Banks’ Rise and Fall
Does a national bank make the US economy more stable or more chaotic? Video created with the Bill of Rights Institute to help students ace their exams. This is the third video in a series of nine with Professor Brian Domitrovic, which aim to be a resource for students studying for US History exams and to provide a survey of different (and sometimes opposing) viewpoints on key episodes in U.S. economic history. How do you think we did? SUBSCRIBE: http://bit.ly/2dUx6wg
Hamilton v. Jefferson: The Central Bank Debate [POLICYbrief]
In 1791, two great minds clashed over an issue of constitutional and historical significance. Alexander Hamilton and Thomas Jefferson tried to make the case to President George Washington for and against having a national, central bank. Hamilton saw the central bank as the key to America’s economic future, whereas Jefferson worried about the consolidation of power and thought a central bank was unconstitutional. In this episode of POLICYbrief, two experts--David Cowen, President/CEO of the Museum of American Finance, and Thomas J. DiLorenzo, Professor of Economics at Loyola University--explain and analyze this 200-year-old debate that still has relevance today. As always, the Federalist Society takes no position on particular legal or public policy issues; all expressions of opinion are those of the speaker.
|
The Federal Reserve - 1913
|
The Federal Reserve System is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a series of financial panics led to the desire for central control of the monetary system in order to alleviate financial crises. Wikipedia
The Federal Reserve monitors risks to the financial system and works to help ensure the system supports a healthy economy for U.S. households, communities, ...
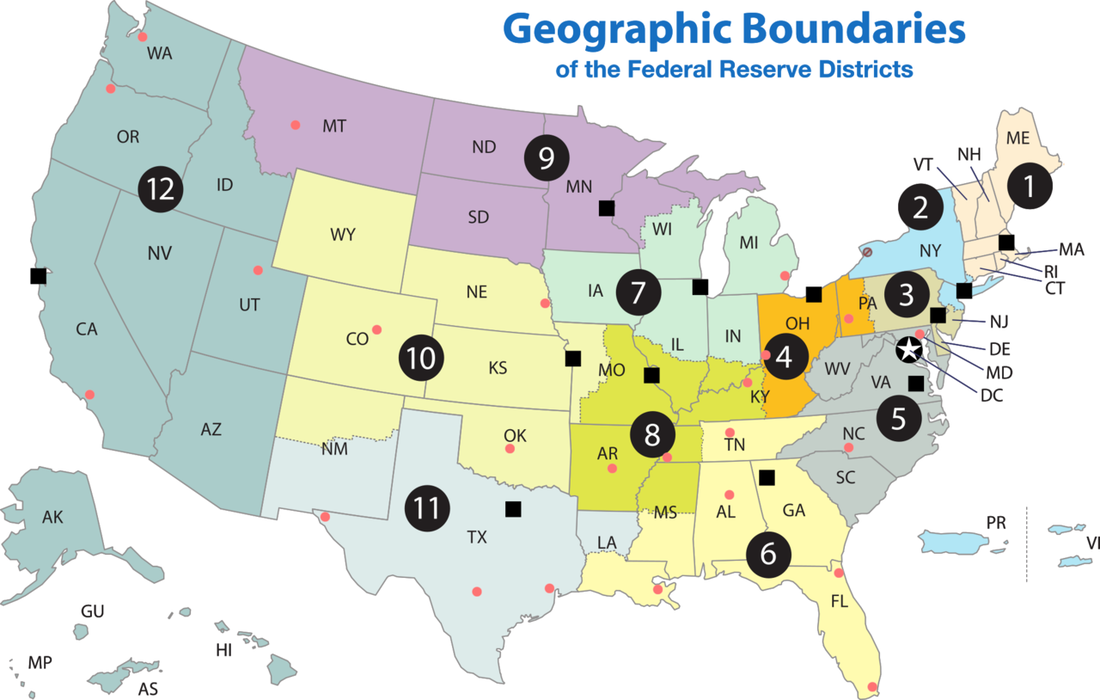
Map of the twelve Federal Reserve Districts, with the twelve Federal Reserve Districts enumerated in black circles and the twelve Federal Reserve Banks marked as black squares. Branches within each district are marked as red circles. The Washington, D.C. headquarters is marked with a star enclosed in a black circle.
Federal Reserve Bank of Boston
The Boston Fed works to promote sound growth and financial stability in New England and the nation. Federal Reserve Bank of New York
Federal Reserve Bank of New York. John C. Williams President Federal Reserve Bank of New York ... New York, NY 10045 (212) 720-5000. Visitor Information. Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia
Philadelphia Fed is on Instagram. Follow our new Instagram account for the latest info, images, and more — spotlighting our work throughout the Third ... Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland
The Center for Inflation Research and the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland invite you to attend Cleveland Fed Conversations on Central Banking, on Tuesday, ... Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond
We're one of 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks working together with the Board of Governors to support a healthy economy. Our job is to serve the American ... Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta
We use cookies on our website to give you the best online experience. Please know that if you continue to browse on our site, you agree to this use. Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago
The homepage of the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago, including recent news, upcoming events, and economic snapshot data. Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis
The St. Louis Fed is central to the nation's economy. It's part of the Federal Reserve System, which includes 12 Federal Reserve banks and the Board of ... Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis
The Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis is pursuing an economy that works for all of us. Serving Montana, North and South Dakota, Minnesota, Wisconsin and ... Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City: Home
Learn more about the history of Black community banks with the latest historical publication from the Kansas City Fed. February 03, 2022 ... Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas - Dallasfed.org
The Dallas Fed promotes a strong financial system and healthy economy for everyone in the Eleventh Federal Reserve District, which ... Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco
The SF Fed is a nonprofit public service institution that supports the economy through research, banking supervision, community development, and education. |
Fed Functions: Conducting Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve, or the Fed, performs five key functions that help promote a healthy economy for all Americans. One of those functions is conducting the nation's monetary policy. Monetary policy is what the Federal Reserve does to accomplish two goals mandated by the U.S. Congress--promoting maximum employment, which means all Americans that want to work are gainfully employed, and promoting stable prices for the goods and services we all purchase. For more information: https://www.federalreserve.gov/aboutt...
In Plain EnglishNeed to learn - or teach someone else - about the Federal Reserve? Have no fear! Whether you're a high school history teacher from Helena or a businessperson from Boise, Buck, our friendly tour guide, will show you around the Federal Reserve System, introducing you to who we are and what we do.
What Does the Federal Reserve Do?
The Federal Reserve, or the Fed, is an important and influential part of the U.S. economy. But what exactly does it do? In this video from the Income Investing course, our Education Coach gives you a simple explanation. Open an account with TD Ameritrade to get access to the Income Investing course and more immersive investor education.
How The Federal Reserve Works (And Who Really Owns It)
In this video, we'll explore how the U.S. Federal Reserve works. You might just be surprised as to who actually owns it!
The Federal Reserve System is the central bank of the United States. It was founded by Congress in 1913 to provide the nation with a safer, more flexible, ...
Latest news and headlines related to the Federal Reserve. ... January's hot inflation may mean the Federal Reserve boosts rates even faster.
News about Federal Reserve (The Fed), including commentary and archival articles published in The New York Times.
|
The Monetary Policy
|
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to control either the interest rate payable for very short-term borrowing or the money supply, often as an attempt to reduce ... Wikipedia
Monetary policy is the control of the quantity of money available in an economy and the channels by which new money is supplied. By managing the money supply, a central bank aims to influence macroeconomic factors including inflation, the rate of consumption, economic growth, and overall liquidity.
Monetary Policy Definition - Investopedia Infographic for Fiscal and Monetary Policy
Below is the full version of the Classroom Economist infographic for Fiscal & Monetary Policy. You can also download this infographic as a PDF for use in your lessons and activities. The Fed Explains Monetary Policy
|
Fiscal & Monetary Policy - Macro Topic 5.1
In this video I overview fiscal and monetary policy and how the economy adjust in the long run. Keep in mind that fiscal and monetary policy shift aggregate demand while waiting for the economy to adjust is a shift in aggregate supply. Thanks for watching. Please subscribe. Need help? Check out the Ultimate Review Packet for FREE: https://www.acdcecon.com/review-packet
Monetary Policy and the Fed- EconMovies #9: Despicable Me
Teachers! I created NEW worksheets for all my EconMovies episodes and for all the Crash Course Economics episodes. If you want to learn more about these worksheets and get some samples, fill out this form: https://forms.gle/1XajQCpkmcdw3Spx5 EconMovies explain economic concepts through movies. In this episode, I use Despicable Me to explain monetary policy, interest rates, and the role of banks in the economy. Good luck studying economics. Oh, and don't mess with Janet Yellen. Thanks for watching. Please subscribe.
|
POST WWII
The Bretton Woods Conference
|
The Bretton Woods Conference, formally known as the United Nations Monetary and Financial Conference, was the gathering of 730 delegates from all 44 Allied nations at the Mount Washington Hotel, situated in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, United States, to regulate the international monetary and financial order after the conclusion of World War II.[1]
Mount Washington Hotel, situated in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, United States
What’s the “Bretton Woods” System?
While today the U.S. is in a trade war with China, the foundations of international trade were laid to avoid war altogether. In this video, Trade Guy Bill Reinsch gives a quick rundown of the Bretton Woods System, the system of global trade that emerged at the end of WWII. Why do we trade with other countries? Watch this video.
The Bretton Woods Institutions are the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). They were set up at a meeting of 43 countries ...
The Bretton Woods systemThe Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial and financial relations among the United States, Canada, Western European countries, Australia, and Japan after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement. Wikipedia
by SK Ghizoni — A new international monetary system was forged by delegates from forty-four nations in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, in July 1944.
The Bretton Woods Agreement and System created a collective international currency exchange regime that lasted from the mid-1940s to the early 1970s. · The ...
|
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an organization of 190 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries.
The IMF is an organization of 189 member countries that works to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international ...
5 Facts About the IMF
The World Bank
The World Bank Group works in every major area of development. We provide a wide array of financial products and technical assistance, and we help countries share and apply innovative knowledge and solutions to the challenges they face.
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. Wikipedia
The World Bank Group: Who We Are, What We Stand For, and How We Get Things DoneThe World Bank is an international organization that provides financing, advice, and research to developing nations to help advance their economies. · The World ...
|
The end of the Bretton Woods system (1972–81)...
The 'Nixon shock'
|
On 15 August 1971, the United States terminated convertibility of the US dollar to gold, effectively bringing the Bretton Woods system to an end and rendering the dollar a fiat currency. ... The Bretton Woods system was over by 1973. The subsequent era has been characterized by floating exchange rates.
Bretton Woods system - Wikipedia Nixon Ends Bretton Woods International Monetary System
On August 15, 1971, President Nixon announced on TV 3 dramatic changes in economic policy. He imposed a wage-price freeze. He ended the Bretton Woods international monetary system. And he imposed a temporary surcharge (tariff) on all imports. The Bretton Woods system was created towards the end of World War II and involved fixed exchange rates with the U.S. dollar as the key currency - but also a role for gold linked to the dollar at $35/ounce. The system began to falter in the 1960s because of an excess of dollars flowing out of the U.S. which foreign central banks had to absorb. A run on gold in 1968 was stemmed by a patch on Bretton Woods known as the two-tier gold system. All of this was ended unilaterally by the Nixon decision. After a brief attempt to create a modified fixed exchange rate system, the world moved to flexible rates.
The Gold Standard, Explained
Before 1974, U.S. dollars were backed by a gold standard. This meant that the federal government could not print more money than it could redeem for gold. While this constrained the federal government, it also provided citizens with a relatively stable purchasing power for goods and services. Today's paper currency has no intrinsic value. It is not based on the value of gold or anything else. Under a gold standard, inflation was really limited. With floating value, or fiat, currency, however, some countries have seen inflation reach extremely high levels—sometimes enough to lead to economic collapse. Gold standards have historically provided more stable currencies with lower inflation than fiat currency. Should the United States return to a gold standard?
|
The Nixon shock was a series of economic measures undertaken by United States President Richard Nixon in 1971, in response to increasing inflation, the most significant of which were wage and price ... Wikipedia
The system dissolved between 1968 and 1973. In August 1971, U.S. President Richard Nixon announced the "temporary" suspension of the dollar's convertibility ...
On August 15, 1971, President Richard M. Nixon announced his New Economic Policy, a program “to create a new prosperity without war.” Known colloquially as the ...
50 years ago, the Bretton Woods system of fixed exchange rates came to a sudden stop. It seemed the end of an era of multilateral and ...
August 15, 2021 marks the 50th anniversary of the day President Richard Nixon “closed the gold window,” ending the postwar Bretton Woods ...
This breakdown of the fixed exchange rate system ended each country's obligation to maintain a fixed price for its currency against gold or other currencies.
On 15 August, 1971, President Richard Nixon shocked the world by ending the Bretton Woods international monetary system the United States ...
Who Killed Capitalism? (Global Crash Documentary) | Real Stories
August 15, 1971 - The day President Nixon declared the dollar would no longer be backed by gold. That decision triggered a ripple effect around the world that forever changed the Capitalist system, allowing governments to print as much money has they’d like and drowning nations with massive debt. The effects of those policies are being felt today - causing huge market crashes, increasing the wealth gap and inflating the price of goods and services while wages remain relatively stagnant.
|
The United States Dollar,
the world's reserve currency
|
Reserve currency - Wikipedia
United States dollar — The United States dollar is the most widely held currency in the allocated reserves, representing about 61% of international ... Why is the dollar so powerful? | CNBC Explains
For more than seven decades, the United States dollar has been the world’s reserve currency, with a majority of international transactions using the greenback. CNBC’s Uptin Saiidi explains how it became so strong and explores whether its position could be threatened.
What is a reserve currency? — The dollar's role as the primary reserve currency for the global economy allows the United States to borrow money more easily ...
by C Bertaut One measure of confidence in a currency as a store of value is its usage in official foreign exchange reserves. As shown in Figure 2, the dollar ...
For example, in the year 1900, the U.S. dollar and pound sterling made up 0% and 62% of global reserves respectively. But fast forward to 2020, ...
|
Why the US dollar is the king of currencies
The dollar's dominance as the primary currency for international trade has given the US a considerable advantage in financial markets for decades. But how did the dollar get its prominence? And are its days numbered?
What if the DOLLAR Was Still Pegged to GOLD | Gold Standard | ENDEVR Explains
Every once in a while, the gold standard goes back into fashion. The world has moved on from currencies attached to the precious metal for 50 years, but discussions around the topic are more vivid than ever. To understand why going back to the gold standard is still appealing to some people we need to dive into what are the disadvantages and advantages of the system.
|
THE FUTURE?
World Economic Forum
Global Financial and Monetary Systems in 2030
This council looked at the future of the Financial and Monetary systems, comprising the following elements: - Evolving regulatory requirements. - Innovating to rebuild trust and stability in the financial system. - The need for a new underlying financial system blueprint. - Increasing access to and use of financial services. - Harnessing data to benefit risk management and customer interaction. - Technological impact on the financial services ecosystem. - System interconnectedness and evolving market risks. Council co-chairs: Axel Lehmann (UBS) and Cecilia Skingsley (Riksbank) Council Manager: Elaine Smith (World Economic Forum)
|
Resetting Digital Currencies Part 1 | DAVOS AGENDA 2021
#WorldEconomicForum #DavosAgenda2021 #DigitalCurrencies
COVID-19 has accelerated the long-term shift from cash, with an 8% increase in non-cash payments in the euro area in 2020. Meanwhile, central bank digital currencies are emerging, potentially transforming how people use money worldwide. What policies, practices and partnerships are needed to leverage the opportunities posed by the rise of digital currencies? Speakers: Sheila Warren, Elizabeth Rossiello, Hikmet Ersek, Andrew Bailey, Her Majesty Queen Máxima of the Netherlands, Glenn H. Hutchins |
Predictions
The Future of Money - New Mini Documentary
Right now, you have many options if you need to pay for something, you can pay with cash, with your atm card or digitally with tons of different apps. You can even pay with bitcoin or cryptocurrency. With so many rapid changes and so many companies competing for dominance in the financial sector, the future of money is exciting. #Future #Money #Technology
The Future of Money in the Digital Age
The Peterson Institute for International Economics (PIIE) and Princeton University’s Bendheim Center for Finance cohost the conference “The Future of Money in the Digital Age” on October 16, 2019. Lael Brainard, member of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, delivers the keynote address on current developments in digital currency and policy implications. Markus K. Brunnermeier, Edwards S. Sanford Professor at Princeton University, presents his recent paper “The Digitization of Money,” followed by a high-level panel with Martin Wolf, chief economics commentator at the Financial Times; Stefan Ingves, governor of the Riksbank; Simon Potter, PIIE nonresident senior fellow; and Hyun Song Shin, head of research at the Bank for International Settlements (BIS). For more information, visit: https://www.piie.com/events/future-mo...
|
How we'll earn money in a future without jobs | Martin Ford
Machines that can think, learn and adapt are coming -- and that could mean that we humans will end up with significant unemployment. What should we do about it? In a straightforward talk about a controversial idea, futurist Martin Ford makes the case for separating income from traditional work and instituting a universal basic income.
The future of money | Neha Narula
What happens when the way we buy, sell and pay for things changes, perhaps even removing the need for banks or currency exchange bureaus? That's the radical promise of a world powered by cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. We're not there yet, but in this sparky talk, digital currency researcher Neha Narula describes the collective fiction of money — and paints a picture of a very different looking future.
|
Cryptocurrency (Digital Currencies)
|
A cryptocurrency, crypto-currency, or crypto is a collection of binary data which is designed to work as a medium of exchange. Wikipedia
Cryptocurrency Definition - Investopedia
A cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that is secured by cryptography, which makes it nearly impossible to counterfeit or double-spend. What Is Cryptocurrency? Beginners Guide to Digital Cash
A cryptocurrency (or “crypto”) is a form of payment that can circulate without the need for a central monetary authority such as a government or bank. History of Cryptocurrency
A short amateur documentary on the history of cryptocurrency, including Bitcoin.
Bitcoin Documentary | Crypto Currencies | Bitcoins | Blockchain | Digital Currency | Money | GoldBitcoin: The End Of Money As We Know It traces the history of money from the bartering societies of the ancient world to the trading floors of Wall St. The documentary exposes the practices of central banks and the dubious financial actors who brought the world to its knees in the last crisis. It highlights the Government influence on the money creation process and how it causes inflation. Moreover, this film explains how most money we use today is created out of thin air by banks when they create debt. Epic in scope, this film examines the patterns of technological innovation and questions everything you thought you knew about money. Is Bitcoin an alternative to national currencies backed by debt? Will Bitcoin and cryptocurrency spark a revolution in how we use money peer to peer? Is it a gift to criminals? Or is it the next bubble waiting to burst? If you trust in your money just as it is - this film has news for you.
What Is Cryptocurrency? Beginners Guide to Digital Cash
To buy cryptocurrencies, you'll need a “wallet” — an online app that can hold your currency. Generally, you create an account on an exchange, and then you can transfer real money to buy cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum. Here's more on how to invest in Bitcoin. Could digital currencies put banks out of business? | The Economist
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have been billed as a major disruptor to finance. But digital currencies issued by governments might be even more radical—they may even threaten the future of traditional banking. Read our special report, “The Future of Banking” : https://econ.st/3tuTT8y
|
Bitcoin: How Cryptocurrencies WorkFrom Elon Musk to your grandma, we all know about the cryptocurrency Bitcoin, but how does it actually work?
The History Of Cryptocurrency In 10 Minutes: From Nothing To Something
How Cryptocurrency ACTUALLY works.
Bitcoin, Dogecoin, Ethereum, NFT's, all explained in one simple guide! Do consider subscribing if you enjoyed!
Why Buy Cryptocurrency? The Ultimate Guide
Cryptocurrency is a fundamental shift in the nature of money. It is much more than just a way to make a quick buck or as a way to diversify your portfolio. I simplify things for myself in the cryptocurrency space by splitting coins into three categories.
Bitcoin came first and because of its unique properties it is arguably the... www.hardmoneyhistory.com/why-buy-cryptocurrency/ Bitcoin and blockchain 101: Why the future will be decentralized | Big Think
We've all heard terms like Bitcoin, blockchain, and cryptocurrency being thrown around in the past few years, but what do they mean? Consider this your crash course. Experts from across the spectrum of money and tech provide a history of commerce dating back tens of thousands of years, explain what blockchain and Bitcoin are and how they work, and offer insights into the differences between centralized and decentralized systems. Because blockchain is incredibly difficult to hack, it has massive implications for elections, banking, shipping, land ownership—any domain where corruption is rampant. While the technology may feel abstract now, programmer Brian Behlendorf compares it to explaining the concept of email to people in 1993. One day, blockchain will be a seamless part of our lives. Check Tony Saldanha's book "Why Digital Transformations Fail: The Surprising Disciplines of How to Take Off and Stay Ahead" at https://amzn.to/36iaOCH
|