ODE
MIDDLE SCHOOL (Grade 7)
WORLD STUDIES
World Studies from 750 B.C. to 1600 A.D.: Ancient Greece to the First Global Age
The seventh grade year is an integrated study of world history, beginning with ancient Greece and continuing through global exploration. All four social studies strands are used to illustrate how historic events are shaped by geographic, social, cultural, economic and political factors. Students develop their understanding of how ideas and events from the past have shaped the world today.
Project Based Learning Resources:
|
Buck Institute for Education: bie.org
edutopia: Project-Based Learning ASCD: Seven Essential for Project-Based Learning Scholastic: The Power of Project Learning NEA: Research Spotlight on Project-Based Learning Kathy Schrock: Authentic Learning Edmodo: Project Based Learning |
Historical Thinking and Skills
1. Historians and archaeologists describe historical events and issues from the perspectives of people living at the time to avoid evaluating the past in terms of today’s norms and values.
- Development of historical thinking concepts began in earlier grades by having students look at primary source documents to understand that multiple sources and perspectives are needed to build a historical narrative.
- Historians and archaeologists provide an accurate account and assessment of a historical event. This requires them to avoid the influence of current norms and values in interpreting and evaluating the past. They generally attempt to describe events through the perspectives of those living at the time. As students examine a historian or archaeologist’s interpretation of an event, students should look to see how they meet this standard.
- By having students critically evaluate diaries, letters, eyewitness accounts, archaeological artifacts and architecture of particular moments in time, they develop an understanding that history is interpreted. They also become active participants in historical investigation.
What are Primary Sources? (A Time Travel Adventure)What are Primary Sources? Go on a time travel adventure to explore history and discover at least ten types of primary sources. Perfect for elementary or middle school social studies/history classes, students will understand the concept of a primary source by the end. Go to www.infotopia.info/primary_sources.html for primary source web sites. Part II will explore questions about Primary Sources.
|
Primary Sources-Part 2, presented by InfotopiaPart 2 of Primary Sources (A Time Travel Adventure) asks students to determine questions to ask about primary sources to determine how primary sources help historians. They become historians examining two primary sources, King Tut's tomb and Anne Frank's diary. Additional resources for more research are given as well.
|
Amazing Resource:
Flocabulary

At the core of Flocabulary is hip-hop, a cultural movement started by black and Latinx youth in New York in the early ’70s. It’s important to understand the history and the socio-cultural and economic circumstances from which hip-hop emerged when teaching with Flocabulary.
Social StudiesOn YouTube:
Flocabulary
176K subscribers Flocabulary is a learning program for all grades that uses educational hip-hop music to engage students and increase achievement across the curriculum. Teachers at 20,000 schools use Flocabulary’s standards-based videos, instructional activities and student creativity tools to supplement instruction and develop core literacy skills. |
Ancient World History
|
Early Civilizations
Ted-Ed: The Silk Road: Connecting the ancient world through tradeView full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-silk-ro...
With modern technology, a global exchange of goods and ideas can happen at the click of a button. But what about 2,000 years ago? Shannon Harris Castelo unfolds the history of the 5,000-mile Silk Road, a network of multiple routes that used the common language of commerce to connect the world's major settlements, thread by thread. Lesson by Shannon Harris Castelo, animation by Steff Lee. Resource: Lesson Plan: Motel of the Mysteries by David Macaulay
Resource: Trekking to Timbuktu: Trade in Ancient West Africa Resource: Silk Road: Spreading Ideas and Innovations Resource: Belief Systems Along the Silk Roads Resource: Effects of the Silk Road |
Silk Road Virtual TourA virtual tour of the Silk Road, from Rome to China, with visits to significant sites along the way.
Animated Map of The Silk Route |
Greece & Rome
2. The civilizations that developed in Greece and Rome had an enduring impact on later civilizations. This legacy includes governance and law, engineering and technology, art and architecture, as well as literature and history. The Roman Empire also played an instrumental role in the spread of Christianity.
Resource: Scholastic - Democracy
Resource: CMC Curriculum Companion - Ancient Greece, C. 800-300BC/BCE
Resource: To Be or Not to Be Democratic
Resource: NEH, EDSITEment - The Alphabet is Historic (4 Lessons)
- The legacy of ancient Greece and Rome is embedded in Western culture. The ideas on governance and law were impacted by the concepts of citizenship and democracy that originated in Ancient Greece. Greece developed a “direct democracy.”
- The Greeks created the astrolabe, the pulley block, the wood screw, ore smelting and casting, and built faster ships. The influence of Ancient Greek art and building designs (e.g., rectangular temples with tall columns all around) can be seen in many cities today. Greek literature inspired the Romans and other writers over the centuries. Greeks also developed the study of history.
- Rome influenced government and law by creating the first republic with elected officials and a system of laws that laid the foundation for many governments. It created a written constitution, a tripartite government (executive, legislative and judicial branches), a system of checks and balances, and a sense of civic duty.
- Roman roads, basilicas, amphitheaters, aqueducts and layouts of cities continue to influence the modern world. Many modern government buildings have Roman styling that includes domes and arches.
- Roman literature and poetry impacted future western civilizations. Rome’s contributions to art include frescoes and sculptures
Resource: Scholastic - Democracy
Resource: CMC Curriculum Companion - Ancient Greece, C. 800-300BC/BCE
Resource: To Be or Not to Be Democratic
Resource: NEH, EDSITEment - The Alphabet is Historic (4 Lessons)
Greece
Ancient Greece 101 | National GeographicFrom artistry to politics, ancient Greece left a considerable impression on world history. Learn why Greek and Roman gods share so many similarities, how the alphabet got its name, and how the legacy of ancient Greece has evolved over thousands of years. ➡ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/NatGeoSubscribe
|
TED-Ed: A day in the life of an ancient Athenian - Robert GarlandView full lesson: https://ed.ted.com/lessons/a-day-in-t... It’s 427 BCE, and the worst internal conflict ever to occur in the ancient Greek world is in its fourth year. Athens is facing a big decision: what to do with the people of Mytilene, a city on the island of Lesbos where a revolt against Athenian rule has just been put down. How did these kinds of decisions get made? Robert Garland outlines a day in the life of Athenian democracy. Lesson by Robert Garland, animation by Zedem Media.
|
Rome
Ancient Rome 101 | National GeographicSpanning over a thousand years, ancient Rome was a civilization of constant evolution. This great empire flourished through innovation and incorporation of the diverse cultures they conquered, such as the adoption of Latin and gladiatorial combat. Learn about the rise and fall of this ancient civilization and how its influence still endures today. ➡ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/NatGeoSubscribe
PBS - Roman City - David MacaulayThe glories of Ancient Rome are explored in ROMAN CITY, based on David Macaulay's acclaimed book. This animated and live-action video recounts life in Verbonia, a fictional city in Gaul. A well-planned town with all modern conveniences, it is threatened by conflict between conquerors and conquered. Macaulay also visits Pompeii, Herculaneum, Ostia, Nimes, Orange, and Rome, to view actual Roman architecture and engineering greatness.
http://www.shoppbs.org/product/index.... What It Was Like to Be a Roman SlaveSlave labor was a huge aspect of Roman life and the Republic depended heavily on free work from human beings who had no rights, no possessions, and were left at the whims of their masters to be worked to death, starved, tortured, and sometimes even killed for the sake of enjoyment. Sure, you may have seen Russell Crowe play one in a movie, but chances are you have no idea just how brutal it really was. Today we’re exploring what it was really like to be a Roman slave. #romanslaves #rome #weirdhistory
|
Ted-Ed: A glimpse of teenage life in ancient RomeView full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/a-glimpse-o...
Welcome to the world of Lucius Popidius Secundus, a 17-year old living in Rome in 73 AD. His life is a typical one of arranged marriages, coming-of-age festivals, and communal baths. Take a look at this exquisitely detailed lesson on life of a typical Roman teenager two thousand years ago. Lesson by Ray Laurence, animation by Cognitive Media. TED Ed: A day in the life of a Roman soldier - Robert GarlandView full lesson: https://ed.ted.com/lessons/a-day-in-t... The year is 15 CE, and the Roman Empire is prospering. Most of the credit will go to the emperor, but this success wouldn’t have been possible without loyal soldiers like Servius Felix. Robert Garland illuminates what life was like for a solider in the Roman army. Lesson by Robert Garland, animation by Brett Underhill.
TED Ed: Four sisters in Ancient Rome - Ray Laurence How did the young, wealthy women of Ancient Rome spend their days? Meet Domitia and her sister Domitia and her sister Domitia and her sister Domitia. Ray Laurence sketches the domestic life of leisure that these young girls lived, despite little recorded information on women from this otherwise well-documented era. Lesson by Ray Laurence, animation by Cognitive Media.
|
Resource: Roman City from David Macaulay
Resource: Rome Technology
Resource: Rome Medicine
Resource: BBC - Meet the Romans
Resource: BBC - Make a model Roman villa
Resource: BBC - Make a Roman mosaic
Resource: BBC - Roman timeline
Resource: NEH, EDSITEment - In Old Pompeii
Resource: Rome Technology
Resource: Rome Medicine
Resource: BBC - Meet the Romans
Resource: BBC - Make a model Roman villa
Resource: BBC - Make a Roman mosaic
Resource: BBC - Roman timeline
Resource: NEH, EDSITEment - In Old Pompeii
The Middle Ages
The Vikings, Byzantine Empire
& European Feudalism
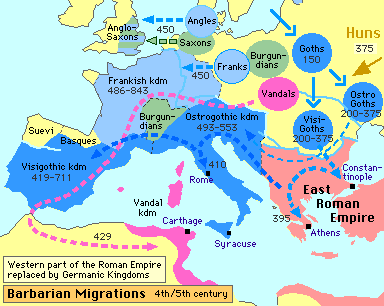
3. Germanic invasions helped to break up the Roman Empire and set the stage for the development of feudal and manorial systems. Later invasions helped establish Mongol dominance in central Asia and led to the destruction of the Byzantine Empire by the Turks
Resource: The Fall of Rome
Resource: Feudalism and the Feudal Relationship
Resource: History for Kids - Feudalism
Resource: BBC- KS3 Bitesize, The Middle Ages
Resource: Mongol Empire
Resource: All Empires - The Mongol Empire
Resource: Asia for Educators, Columbia University - The Mongols in World History
Resource: National Geographic - Mongolian Empire Interactive Map
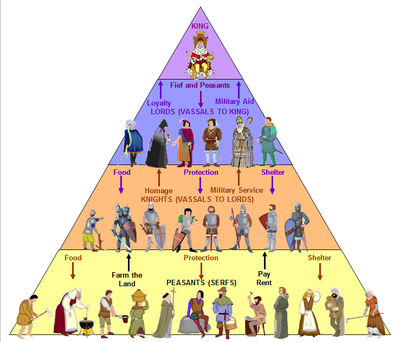
- The breakup of the Roman Empire, hastened by Germanic invasions and the decline of Roman institutions such as a central government, led to the development of feudal and manorial systems.
- Feudalism was the system by which medieval Europeans organized their power and governments. Vassals received land and protection from a lord when they worked and fought for him. It might be understood as a pyramid with the monarch presiding over a hierarchy of less important vassals.
- The manorial system was related to feudalism. It was an economic relationship between the peasants and lord. The peasants worked on land owned by the lord in return for fixed dues in kind, money and services. The manorial system prevailed in many European countries.
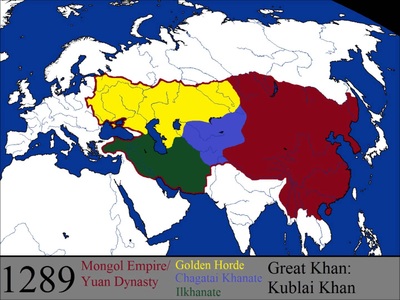
- By the 13th century, the Mongols had invaded and established dominance in Central Asia, China, Persia, Tibet, Iraq, much of Asia Minor and all of southern Russia.
- The Byzantine Empire was invaded by the Ottoman Turks in the 14th and 15th centuries, and finally fell in 1453. Constantinople was the ultimate goal for the Turks since its physical position was very favorable economically, militarily and strategically.
Resource: The Fall of Rome
Resource: Feudalism and the Feudal Relationship
Resource: History for Kids - Feudalism
Resource: BBC- KS3 Bitesize, The Middle Ages
Resource: Mongol Empire
Resource: All Empires - The Mongol Empire
Resource: Asia for Educators, Columbia University - The Mongols in World History
Resource: National Geographic - Mongolian Empire Interactive Map
CNN.com - Millennium: A Perspectives Series

A THOUSAND YEARS OF HISTORY. EXPERIENCE THE PEOPLE. THE EVENTS AND ACHIEVEMENTS. THAT SHAPED THE WORLD:
www.cnn.com/SPECIALS/1999/millennium/
www.cnn.com/SPECIALS/1999/millennium/
ABOUT THE SERIES
MILLENNIUM offers a panoramic sweep over the last 1,000 years and the people, events and achievements that shaped the world.
The 10, one-hour episodes of MILLENNIUM are extraordinary in their range of vision and compelling in their presentation. Yet MILLENNIUM is neither chronological nor all-encompassing. Instead, it is eclectic, a pastiche of things great -- or small -- that sculpted the world.
Each of the 10 episodes of MILLENNIUM focuses on a single century, brought to life by five vignettes from five different locations worldwide.
Episode 1: 11th century - Century of the Sword
Episode 2: 12th century - Century of the Axe
Episode 3: 13th century - Century of the Stirrup
Episode 4: 14th century - Century of the Scythe
Episode 5: 15th century - Century of the Sail
Episode 6: 16th century - Century of the Compass
Episode 7: 17th century - Century of the Telescope
Episode 8: 18th century - Century of the Furance
Episode 9: 19th century- Century of the Machine
Episode 10: 20th century - Century of the Globe
*Episodes 1-6 applicable for Grade 7 curriculum
Inspired by Felipe Fernandez-Armesto's book, "Millennium," and filmed in 28 countries, the series is as geographically far-ranging as the world it covers. Its producers and crews spent more than two years and traveled 100,000 miles gathering footage. MILLENNIUM reconstructs the visual images of past ages using this footage, along with vivid re-enactments and computer-generated graphic animation.
MILLENNIUM is peopled with the interesting and the provocative, among them: Native Americans who built canyon housing complexes and Ethiopians who carved churches from solid rock in the 12th century; Genghis Khan, whose 13th century Mongol warriors conquered and united central Asia; Timur, who rose from sheep-stealer to conqueror and expanded Islam's empire in the 14th century; Christopher Columbus, whose 15th century voyage changed the world; African slaves taken from their homeland to serve the Americas' new colonies in the 17th century; French explorers who endured the Arctic's cold in the 18th century; Charles Darwin, whose theories of evolution challenged the 19th century's religious certainties; and the 20th century's superstars, including Charlie Chaplin and Princess Diana.
Woven into MILLENNIUM's tapestry are details that will probably surprise and may enlighten. Eleventh century China had printing, gunpowder and the waterclock. One thousand years ago, two Japanese women wrote two of the world's greatest books, "The Tales of Genji" and "The Pillow Book of Sei Shonagon." In the 15th century, Chinese Admiral Zheng He's naval fleet boasted the largest wooden ships ever built. In 18th century France, the game of chess symbolized revolution because a pawn can capture a king.
MILLENNIUM offers a panoramic sweep over the last 1,000 years and the people, events and achievements that shaped the world.
The 10, one-hour episodes of MILLENNIUM are extraordinary in their range of vision and compelling in their presentation. Yet MILLENNIUM is neither chronological nor all-encompassing. Instead, it is eclectic, a pastiche of things great -- or small -- that sculpted the world.
Each of the 10 episodes of MILLENNIUM focuses on a single century, brought to life by five vignettes from five different locations worldwide.
Episode 1: 11th century - Century of the Sword
Episode 2: 12th century - Century of the Axe
Episode 3: 13th century - Century of the Stirrup
Episode 4: 14th century - Century of the Scythe
Episode 5: 15th century - Century of the Sail
Episode 6: 16th century - Century of the Compass
Episode 7: 17th century - Century of the Telescope
Episode 8: 18th century - Century of the Furance
Episode 9: 19th century- Century of the Machine
Episode 10: 20th century - Century of the Globe
*Episodes 1-6 applicable for Grade 7 curriculum
Inspired by Felipe Fernandez-Armesto's book, "Millennium," and filmed in 28 countries, the series is as geographically far-ranging as the world it covers. Its producers and crews spent more than two years and traveled 100,000 miles gathering footage. MILLENNIUM reconstructs the visual images of past ages using this footage, along with vivid re-enactments and computer-generated graphic animation.
MILLENNIUM is peopled with the interesting and the provocative, among them: Native Americans who built canyon housing complexes and Ethiopians who carved churches from solid rock in the 12th century; Genghis Khan, whose 13th century Mongol warriors conquered and united central Asia; Timur, who rose from sheep-stealer to conqueror and expanded Islam's empire in the 14th century; Christopher Columbus, whose 15th century voyage changed the world; African slaves taken from their homeland to serve the Americas' new colonies in the 17th century; French explorers who endured the Arctic's cold in the 18th century; Charles Darwin, whose theories of evolution challenged the 19th century's religious certainties; and the 20th century's superstars, including Charlie Chaplin and Princess Diana.
Woven into MILLENNIUM's tapestry are details that will probably surprise and may enlighten. Eleventh century China had printing, gunpowder and the waterclock. One thousand years ago, two Japanese women wrote two of the world's greatest books, "The Tales of Genji" and "The Pillow Book of Sei Shonagon." In the 15th century, Chinese Admiral Zheng He's naval fleet boasted the largest wooden ships ever built. In 18th century France, the game of chess symbolized revolution because a pawn can capture a king.
The Vikings
Vikings For Kids // History For Kids
Suitable for teaching 7-11s. This Lesson shows you the life of a Viking, an old Viking Town in Sweden. This is a fantastic video to start off a Viking Teaching Unit. What do you know about the Vikings? Well, the stuff you've heard about them may not be true. The Vikings were some of the greatest travellers of their time, and they weren't always traveling to steal. ===================== Join me in the cold, wintery town of Uppsala, Sweden. Here, we visit an ancient Viking Village to learn all about their culture, daily life, and if they were as bad as we think they were. Come with me to see where the Viking People got their reputation. Try to stay warm as we go on this adventure together!
http://www.destinationuppsala.se/en/T... TED-Ed: What's so special about Viking ships? - Jan BillExplore the history and technology of Viking longships, which helped the Scandinavians conquer trade routes and new territories. -- As the Roman Empire flourished, Scandinavians had small settlements and no central government. Yet by the 11th century, they had spread far from Scandinavia, gaining control of trade routes throughout Europe, conquering kingdoms as far as Africa, and building outposts in North America. What was the secret to their success? Jan Bill dives into the history of the formidable Viking longship. Lesson by Jan Bill, directed by TOTEM Studio.
|
The Vikings - In a nutshell
Vikings, Norse seafarers who left their homelands in Scandinavia to raid, trade, explore, and settle in wide areas of Europe, Asia, and the North Atlantic islands, from the late 8th to the mid-11th centuries. Learn it all in a Nutshell. The Vikings were groups of warriors from Scandinavia who between the 8th and 11th centuries left their homes -in order to raid and settle in Europe, Asia and the North Atlantic --during a period known as "the Viking Age".
Watch: An Incredible Viking Voyage—Made Entirely of Paper | National Geographic
Watch a young viking learn how to identify the proper tree to build a ship, nail the craft together, and set off on a journey around Europe.
How They Did It - Growing Up VikingA history documentary on what it was like to grow up Viking
|
The Byzantine Empire
History Summarized: Byzantine Empire — Beginnings
It's Rome! It's Greece! It's... The Byzantine Empire! Check out how late Imperial Rome transformed in the centuries from Constantine to Justinian, as it evolved into a new and unique iteration of Roman civilization. Watch as Byzantine craftsmen revolutionize artwork by throwing a megaton of gold onto every last mosaic in the Mediterranean, and radically reimagine architecture by asking "But what if *dome*?"
TED Ed: The rise and fall of the Byzantine Empire - Leonora NevilleView full lesson: https://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-rise-a...
Most history books will tell you that the Roman Empire fell in the fifth century CE, but this would’ve come as a surprise to the millions who lived in the Roman Empire through the Middle Ages. This Medieval Roman Empire, today called the Byzantine Empire, began when Constantine, the first Christian emperor, moved Rome's capital. Leonora Neville details the rise and fall of the Byzantine Empire. Lesson by Leonora Neville, animation by Remus & Kiki. Ted-Ed: It's a church. It's a mosque. It's Hagia Sophia.View full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/it-s-a-chur...
If walls could talk, Turkey's Hagia Sophia would have an abundance of stories to tell. Once a church, then a mosque, and now a museum, this world marvel has stood the test of time and war, surviving centuries of conquest by some of history's greatest empires. Kelly Wall takes us through the history of each layer of this great jewel of human desire. Lesson by Kelly Wall, animation by Andrew Foerster. |
TED-Ed: The city of walls: Constantinople - Lars BrownworthThe world owes much of its cultural legacy to Constantinople's walls. When Constantinople was under seige by neighboring enemies, the Roman city's elaborate system of moats, outer walls, and inner walls stood tall. Surviving numerous fire attacks, the walls were eventually brought down by more modern tools of warfare, but, thankfully, classical culture survived. Lesson by Lars Brownworth, animation by Woland.
The Fall of ConstantinopleHow exactly did the Roman Empire come to an end? Well, in today's animated educational cartoon we are looking at how the Byzantine Empire overtook the incredible Constantinople as their new capital city, making the final nail in the coffin for the Roman Empire.
They Might Be Giants - Istanbul
|
European Feudalism
The Middle Ages in 3 1/2 minutesAn animated timeline from the book 'Science: a Discovery in Comics' by Margreet de Heer.
More information:http://margreetdeheer.com/eng/science... There's also an animated timeline of the History of the Earth: http://youtu.be/8qnnoePeHlk What was Feudalism? | 4 Minute HistoryIn this video we explain the concept of Feudalism, its origins and its eventual demise in Europe. Ideal for GCSE and A Level History students.
City life in the middle ages - Medieval Madness
Have you ever wondered what it was like to live in a medieval city?
PBS - Castle - David MacaulayCASTLE combines colorful animation with live-action documentary sequences to tell the story of a 13th-century Welsh castle. Author David Macaulay, who wrote and illustrated the best-selling book of the same title, leads viewers on a castle tour, explaining its cultural and sociological significance and its architectural design. Detailed animation dramatizes the building of the castle and portrays the lifestyle of the early inhabitants. http://www.shoppbs.org/product/index....
Ted-Ed: The past, present and future of the bubonic plagueView full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-past-pr...
The bubonic plague, which killed around 1/5 of the world’s population in the 14th century, is still around today -- but it now claims only a few thousand lives each year. How did that number shrink so drastically? Sharon N. DeWitte investigates the causes and effects of the black death and explains how knowing this information can help us prepare for any future outbreaks of the disease. Lesson by Sharon N. DeWitte, animation by Steff Lee. History Summarized: The Crusades
Making a video exclusively about the crusades? That's a bold strategy, Blue, let's see how it pays off. RELEVANT LINKS:
History Summarized: Islam: https://youtu.be/Uvq59FPgx88 History Summarized: Christianity: https://youtu.be/A86fIELxFds History Summarized: Judaism: https://youtu.be/aKB6WduDwNE History Summarized: Christianity, Judaism, and the Muslim Conquest: ****Link, when you get it*** History Summarized: Venice (Part 2): https://youtu.be/byMleAJ5kRs?t=4m25s History Summarized: Byzantine Empire: https://youtu.be/-ucHQVu8Dw0?t=6m15s History Summarized: Abrahamic Religious Philosophy: https://youtu.be/B7myRRt0Mn8 |
How Much It Sucked to Be a Medieval SerfAs draining as the 40 hour work week can be, we should really count our blessings for labor laws and HR departments. Picture yourself in the daily life of a serf: You work as much as your boss insists, you live in your boss’s house, and you can’t leave your boss’s house - even if they decide to sell it to someone else. You will live there forever, and your children will, as well.
#Serf #FeudalSystem #WeirdHistory What It Was Like to be a Knight During Medieval TimesWhen we think of knights during the medieval times, we think of valiant men who chose to defend their honor in feats of jousting, chivalry, and dragon slaying. But that’s not exactly how it was for the actual knights. Today, we’re exploring What It Was Actually Like to be a Knight During Medieval Times. #Knights #Medieval #Weirdhistory
What Life Was Like In Medieval CastlesDespite what pop culture might have you believe, living in a medieval castle wasn't all that glamorous. If you were one of the lucky ruling class, you got some wine or the occasional hot bath. But with the lack of plumbing, castles smelled pretty ripe. Not to mention rats. So many rats. Today we're getting real about what living in a medieval castle was like, and it's not that pretty. #medievalcastles #middleages #history
Why Do Babies In Medieval Art Look Like Creepy Adults?
Infants in medieval art all have one thing in common: They don't look like babies. Instead, they resemble miniature versions of middle-aged men, sometimes complete with receding hairlines and ripped muscles. Depictions of weird, prematurely aged babies appeared throughout the medieval era and into the Renaissance when the trend (thankfully) started to fade away.
How You Could Have Survived the Black Plague
The Black Death is a plague that changed the world. As the most profound epidemic in human history, the plague claimed the lives of millions, with nearly half of Europe's population perishing from the disease. Some feared they were living through the apocalypse amidst the chaotic upheaval, while others turned to sinful pleasure during the plague to distract from the horror. And as for what happened to victims of the plague, well, it wasn't opportune.
What Life Was Like for a Medieval CrusaderLike any great conflict, the Crusades have been the subject of myths and misinformation for years. While few still believe the propaganda that justified the fighting, various false facts have proliferated over the years, concerning everything from the motivations of the Crusaders to their reception in Arab lands.
|
The Mongols,
China & Japan
4. Mongol influence led to unified states in China and Korea, but the Mongol failure to conquer Japan allowed a feudal system to persist.
Resource: The Japanese Project (Fuedalism)
Resource: History.com - Samurai and Bushido
Resource: PlayBuzz - Who Would You Have Been In Feudal Era Japan?
Resource: Welcome to Edo!
Resource: globaled.org - The Japan Project, Lesson 20 Feudalism
- The Mongols conquered and united most of present day China and Korea for approximately 80 years during the 13th and 14th centuries. This dynasty strengthened trade in China by exporting porcelain and silk.
- Growing opposition to the rule of the foreigners led to the overthrow of the Mongols. Korea and China reverted back to dynasties in their respective countries.
- The Mongols attempted to conquer Japan but were unsuccessful. Japan’s system of feudalism persisted and, over time, led to an insular and isolated society that continued to the 19th century.
Resource: The Japanese Project (Fuedalism)
Resource: History.com - Samurai and Bushido
Resource: PlayBuzz - Who Would You Have Been In Feudal Era Japan?
Resource: Welcome to Edo!
Resource: globaled.org - The Japan Project, Lesson 20 Feudalism
The Mongols
TED Ed: The rise and fall of the Mongol Empire - Anne F. BroadbridgeTrace the rise and fall of the Mongol Empire which, under the leadership of Genghis Khan, became the largest contiguous land empire in history. -- It was the largest contiguous land empire in history— stretching from Korea to Ukraine, and from Siberia to southern China. And was forged on the open plains. In the 12th century, the East Asian steppe was home to scattered groups of nomads who, by 1206, would be united under the innovative leadership of a man named Temujin. Anne F. Broadbridge details the rise and fall of the Mongol Empire.
Lesson by Anne F. Broadbridge, directed by Globizco Studios. |
TED Ed: A day in the life of a Mongolian queen - Anne F. BroadbridgeView full lesson: https://ed.ted.com/lessons/a-day-in-t... As dawn breaks over a moveable city of ten thousand yurts, Queen Boraqchin readies her kingdom for departure to their summer camping grounds. While her husband, the grandson of Genghis Khan, is out raiding, she juggles the duties of managing flocks, family and a city of thousands. Anne F. Broadbridge outlines a day in the life of a Mongolian queen. Lesson by Anne F. Broadbridge, directed by Els Decaluwe.
|
China
Ancient China Part One
Dragons? We've got dragons! We discuss the Yangtze and Yellow River civilization, the Xia, Shang, Zhou, Warring States Period, and Qin. Historian Sima Qian is also covered along with Confucius and Laozi. For information about Ed You Too's adaptive player: https://youtu.be/_9Q2Esef9jE
China Part Two
This video covers the Han Dynasty, the Three Kingdoms, Buddhism in China, the Jin Empire, the Sui, the Tang, the dynastic cycle and corruption.
The 4 Great Inventions that changed the world (China)
Papermaking, gunpowder, printing and the compass. These four inventions have been recognized as catalysts for great civilizations.
Ancient China Explained in 13 Minutes
China today is a country of many controversies. Its industry is booming, but it’s a socialist state. The communist party is the undisputed ruler of the entire nation, with many Orwellian features in its dictatorship. Even Chinese society seems to be rather collectivistic in nature. With the centralized economy, a strong people’s army, and a clear leftist ideology, China today is without a doubt a communist country, which, unlike most of its predecessors, seems to be functioning and here to stay. But despite all that, there is a resemblance between this modern People’s Republic and Imperial China of the past, as the same blood of the red dragon flows through its veins. And though ideology has changed quite substantially, it looks like the philosophy behind it remained the same. So, to understand present-day China, its politics, society, and culture in general, we have to go back to the beginnings of the Chinese civilization.
When China Ruled the Waves (Chinese Dynasty Documentary) | TimelineTold through the eyes of a daring modern day adventurer, this is the story of a unique chapter in the history of one of the world's greatest super-powers. This program chronicles the history of the great Ming Dynasty ‘treasure’ ships. Built in the early 15th century these ships gave China the capability of exploring and perhaps conquering the ‘world’.
|
TED Ed: The history of tea - Shunan TengView full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-history... Tea is the second most consumed beverage in the world after water –– and from sugary Turkish Rize tea to salty Tibetan butter tea, there are almost as many ways of preparing the beverage as there are cultures on the globe. Where did this beverage originate, and how did it become so popular? Shunan Teng details tea’s long history. Lesson by Shunan Teng, animation by Steff Lee.
TED Ed: What makes the Great Wall of China so extraordinary - Megan Campisi and Pen-Pen ChenView full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-makes-... The Great Wall of China is a 13,000-mile dragon of earth and stone that winds its way through the countryside of China. As it turns out, the wall’s history is almost as long and serpentine as its structure. Megan Campisi and Pen-Pen Chen detail the building and subsequent decay of this massive, impressive wall. Lesson by Megan Campisi and Pen-Pen Chen, animation by Steff Lee.
TED Ed: The incredible history of China's terracotta warriors - Megan Campisi and Pen-Pen ChenView full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-incredi... In 1974, farmers digging a well near their small village stumbled upon one of the most important finds in archaeological history – vast underground chambers surrounding a Chinese emperor’s tomb that contained more than 8,000 life-size clay soldiers ready for battle. Megan Campisi and Pen-Pen Chen shares the fascinating history of Emperor Qin Shi Huang. Lesson by Megan Campisi and Pen-Pen Chen, animation by Zedem Media.
TED Ed: The hidden meanings of yin and yang - John BellaimeyView full lesson here: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-hidden-...
The ubiquitous yin-yang symbol holds its roots in Taoism/Daoism, a Chinese religion and philosophy. The yin, the dark swirl, is associated with shadows, femininity, and the trough of a wave; the yang, the light swirl, represents brightness, passion and growth. John Bellaimey explains why we all contain the spirit of yin and of yang -- and how we can achieve a balance of both in our lives. Lesson by John Bellaimey, animation by TED-Ed. |
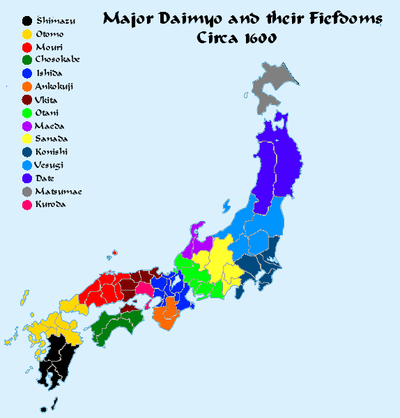
Japan
Ancient Japan Explained in 13 Minutes
Japan, the country of the rising sun, is today known as one of the most prosperous and technologically advanced nations despite not having many natural resources. It is full of hardworking, ethical people that live with a mix of old-time traditions and new-age progressive lifestyles. It’s the land of famed and virtuous samurai warriors, for whom loyalty is everything, and of legendary and adept ninja assassins, capable of bypassing any obstacle. No less famed is Japanese art, unique in its style and form, from short haiku songs to breathtaking watercolor paintings, both amazingly vivid and simplistic in form. It’s the country of Buddhist Zen masters, who were wise and spiritual, symbols of moderation and morality. At the same time, it’s the culture of geishas, who represented indulgence, entertainment, and corporeal desires. Today, it is one of the most liberal and democratic countries, yet it still has an emperor on the throne and a long tradition of shōguns, who were more or less military dictators. All in all, Japan seems to be a country of paradoxes and oppositions, of yin and yang.
🇯🇵 The Shogunate: History of JapanA brief history of the Shogunate system of Japan.
What Life Was Like as a Samurai In Feudal JapanSamurai dominated the country of Japan from the 12th to the 19th century. The fierce, disciplined warriors lived according to the bushido code, an unwritten set of rules and norms based in loyalty, sacrifice, bravery, and honor, remembered popularly as samurai code. Along with the code came samurai traditions and customs that defined their physical appearance, sexual relationships, how they killed and how they died. Just like pirates cherished their earrings and Vikings dyed their hair, samurai demonstrated their dedication to the code and to their lifestyle in some unique ways.
|
TED Ed: Gyotaku: The ancient Japanese art of printing fish - K. Erica DodgeView full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/gyotaku-the...
How did fishermen record their trophy catches before the invention of photography? In 19th century Japan, fishing boats were equipped with rice paper, sumi-e ink, and brushes in order to create gyoktaku: elaborate rubbings of freshly caught fish. K. Erica Dodge recounts the story of this competitive fishing culture, plus some tips on how to make your very own etchings. Lesson by K. Erica Dodge, animation by Franco Barroeta. TED Ed: Kabuki: The people's dramatic art - Amanda MattesView full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-makes-...
The Great Wall of China is a 13,000-mile dragon of earth and stone that winds its way through the countryside of China. As it turns out, the wall’s history is almost as long and serpentine as its structure. Megan Campisi and Pen-Pen Chen detail the building and subsequent decay of this massive, impressive wall. Lesson by Megan Campisi and Pen-Pen Chen, animation by Steff Lee. The Samurai
The samurai warrior trained by serving under his master and following a strict code called bushido - ‘the way of the warrior’.
Life in Edo Japan (1603-1868)
Let's take a tour of Edo, Japan's capital (now Tokyo) during the Tokugawa Period.
|
Islamic Civilization
5. Achievements in medicine, science, mathematics and geography by the Islamic civilization dominated most of the Mediterranean after the decline of the Roman Empire. These achievements were introduced into Western Europe as a result of the Muslim conquests, Crusades and trade, influencing the European Renaissance
- In grade six, students learned general knowledge about world religions, including Islam, as they relate to the overall culture of a region. This year, the study focuses on the impact of Islamic civilization as it spread throughout most of the Mediterranean in the period following the fall of Rome and its later impact on the European Renaissance.
- Muslims made contributions in anatomy, physiology and pharmacology, and in medicine with the creation of a medical textbook. Islamic advances in astronomy aided their development of a calendar and improvement of the astrolabe.
- They helped establish chemistry as a distinct branch of science and trigonometry as a distinct branch of mathematics. Muslims produced world maps and, later, served as navigators for European explorers.
- Islamic achievements spread when Muslim rulers conquered most of the Middle East and parts of southern Europe, and from the trade that grew as a result of the Crusades.
- As the golden age of Islam was waning in the 15th century, its impact on learning and culture was evident in the Italian Renaissance that began to flourish.
How Islam Began - In Ten MinutesHow Islam began in under ten minutes? Not a problem. The turbulent tale is told against the clock, with all the names, dates and events on a timeline.
Why Was the Islamic Golden Age of Science… Golden?
Around 750-1250 CE, the Islamic empire made incredible scientific advancements that still influence many fields of research today. What we know about some of the great minds of that time, as well as what we’ve learned from modern studies, suggest that the diversity of the scholars and their knowledge during that period might have played a big role in making that golden age what it was.
Islam in brief
An introduction to the teachings and history of Islam, from Harvard University. From our free online course, “Islam Through Its Scriptures”: https://www.edx.org/course/islam-thro... — Subscribe to our channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCKJy...
|
Islamic Golden Age - Philosophy and HumanitiesThe new Kings and Generals animated historical documentary series will describe the Golden age of Islam. This particular video will cover the philosophy and humanities of the caliphate.
Islamic Golden Age: Scientific Method DOCUMENTARY
Kings and Generals animated historical documentary series on the Golden Age of Islam continues with a video describing the Muslim contributions to the scientific method, math, physics and chemistry.
TED Ed: The complex geometry of Islamic design - Eric BrougView full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-complex...
In Islamic culture, geometric design is everywhere: you can find it in mosques, madrasas, palaces, and private homes. And despite the remarkable complexity of these designs, they can be created with just a compass to draw circles and a ruler to make lines within them. Eric Broug covers the basics of geometric Islamic design. Lesson by Eric Broug, animation by TED-Ed. |
The Renaissance
6. The Renaissance in Europe introduced revolutionary ideas, leading to cultural, scientific and social changes.
- Europe in the 14th through 17th centuries experienced a period in which a rebirth of Greco-Roman ideas impacted culture, science and society. The Renaissance began in Italy and spread to other European countries. The social changes that took place during the Renaissance transformed every aspect of European society.
- The rebirth that took place was most evident in the arts, literature and education. Painters and sculptors depicted naturalistic scenes and realistic details of individuals. Some experimented in the use of perspective. Many writers focused on ideas for reforming society.
- It also was a period in which conventional scientific theories were challenged. The revolutionary ideas relating to the study of the earth and its place in the universe placed those who espoused them in conflict with the Roman Catholic Church.
|
Resource: The Renaissance
Resource: Kids Discover - Renaissance Resource: The Renaissance Connection Resource: Annenberg Learner - Renaissance Resource: Eyewitness to History Middle Ages and The Renaissance Resource: NEH, EDSITEment - Galileo and the Inevitability of Ideas Resource: NEH, EDSITEment - Galileo: Revealing the Universe Dropping In On Renaissance ArtistsThis program is part of the DROPPING IN ON ARTISTS Series. Students of all ages will be introduced to the artists' styles and learn about their lives in these amusing and informative programs. Playful animation shows the life of the artist, and gives insight into the creative inspiration for their masterworks. In this program join Puffer as he drops in on Florence, Italy, the birthplace of the Renaissance, and learns about the art of Michelangelo, da Vinci, and Raphael
CSI: Florence
www.mrroughton.comCSI: Florence
In a church on Easter Sunday of 1478 an attempt was made to wipe out the Medici dynasty in one single attack. The attack was only half successful. We know who the attackers were but we do not know who organized the clearly well-planned attack. You will attempt to find out by decoding a secret letter, listening to witness testimony and exploring why some people might have been angry enough at the Medici to commit murder. Your suspects include a powerful rival family, a former employee of the Medici and the pope himself! CSI FlorenceIntro video for the CSI: Florence lab for Mr. Roughton's social studies class.
Historian on SixtusExhibit for the CSI: Florence lab from www.mrroughton.com. Visit the site for the rest of the exhiibits
Duke of Urbino TestimonyExhibit for the CSI: Florence lab from www.mrroughton.com.
In 1498 an attempt was made to wipe out the Medici dynasty. This brazen attack may have been set into motion by the pope himself. Examine the clues below to find out who was behind it.
Time: 45 minutes Materials: video player, print-outs below Set-up: Print out each of the exhibits in the files below. It helps to have 5 or 6 copies of each. Begin by showing the intro video and possibly Exhibit A then disperse students to visit each of the exhibits. These 3 files below have all the exhibits and handouts for students. Investigation Journal I CSI: Florence Part 1 I CSI: Florence Part 2 Please visit the following link for the rest of Mr. Roughton's amazing efforts and access to other wonderful resources: http://www.mrroughton.com/history-mystery-labs/csi-florence |
Exploring the Renaissance
A specially commissioned short animation on the Renaissance for primary school students, created by the National Gallery of Ireland.
TED Ed: Da Vinci's Vitruvian Man of math - James EarleView full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/da-vinci-s-... What's so special about Leonardo da Vinci's Vitruvian Man? With arms outstretched, the man fills the irreconcilable spaces of a circle and a square -- symbolizing the Renaissance-era belief in the mutable nature of humankind. James Earle explains the geometric, religious and philosophical significance of this deceptively simple drawing.
Lesson by James Earle, animation by TED-Ed. Ted-Ed: The many meanings of Michelangelo's Statue of DavidView full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-many-me...
We typically experience classic works of art in a museum, stripped of their original contexts, but that serene setting can belie a tumultuous history. Take Michelangelo's statue of David: devised as a religious symbol, adopted as a political emblem, and later iconized for its aesthetic beauty. James Earle walks us through the statue's journey, to show how art gains layers of meaning over time. Lesson by James Earle, animation by Avi Ofer. SPOTLIGHT: Renaissance Architecture | Encyclopaedia BritannicaAn overview of Renaissance architecture.
How an Amateur Built the World's Biggest DomeIn 1418, Filippo Brunelleschi was tasked with building the largest dome ever seen at the time. He had no formal architecture training. Yet experts still don't fully understand the brilliant methods he used in contructing the dome, which tops the Santa Maria del Fiore cathedral in Florence, Italy. ➡ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/NatGeoSubscribe #NationalGeographic #WorldsBiggestDome #WorldRecords
|
The Reformation
7. The Reformation introduced changes in religion including the emergence of Protestant faiths and a decline in the political power and social influence of the Roman Catholic Church.
- The Reformation was an outgrowth of the Renaissance. It was a period in the 16th and 17th centuries that led to the decline in the political power and social influence of the Roman Catholic Church.
- The Reformation began in Germany and was an attempt to bring reform to some of the policies and doctrines of the Roman Catholic Church (e.g. use of indulgences, practice of nepotism). Reform efforts were met with resistance from the Roman Catholic Church and led the creation of a new Protestant denomination (Lutheran). Soon, other Protestant denominations developed across Europe over different issues and under different circumstances (e.g., Anglican, Presbyterian, Anabaptists)
History 101: The Protestant Reformation | National GeographicWho was Martin Luther? What is the Reformation and why does it matter? Roughly 500 years ago, Luther is said to have nailed his 95 Theses on the door of the Castle Church in Germany. With the help of the printing press, this 16th century protest against corruption in the Catholic Church would drastically change the course of Christianity - and history itself. ➡ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/NatGeoSubscribe
A Fun, Animated History of the Reformation and the Man Who Started It All | Short Film ShowcaseOn October 31, 1517, a rebellious German monk named Martin Luther is said to have nailed his Ninety-Five Theses to the door of Castle Church. This simple act of protest sparked a religious revolution that would split Western Christianity and shake the foundations of Europe's cultural identity.
Resource: PBS - Martin Luther
Resource: bio - Martin Luther Resource: The 95 Theses Resource: Christian Classics Ethereal Library, Martin Luther Resource: '95 Theses' - rap music video Resource: 95 Theses - Martin Luther Rap Resource: Luther Rap |
Martin LutherMartin Luther, the 95 Theses and the Birth of the Protestant Reformation
TED Ed: History vs. Henry VIII - Mark Robinson and Alex GendlerView full lesson: https://ed.ted.com/lessons/history-vs... He was a powerful king whose break with the church of Rome would forever change the course of English history. But was he a charismatic reformer who freed his subjects from a corrupt establishment or a bullying tyrant who used Parliament for his own personal gain? Mark Robinson and Alex Gendler put this controversial figure on trial in History vs. Henry VIII.
Lesson by Mark Robinson and Alex Gendler, directed by Brett Underhill. Feature History - Thirty Years' War
Hello and welcome to Feature History, featuring religious conflict, tragic war, and a really nifty collaboration with Jabzy.
|
First Global Age
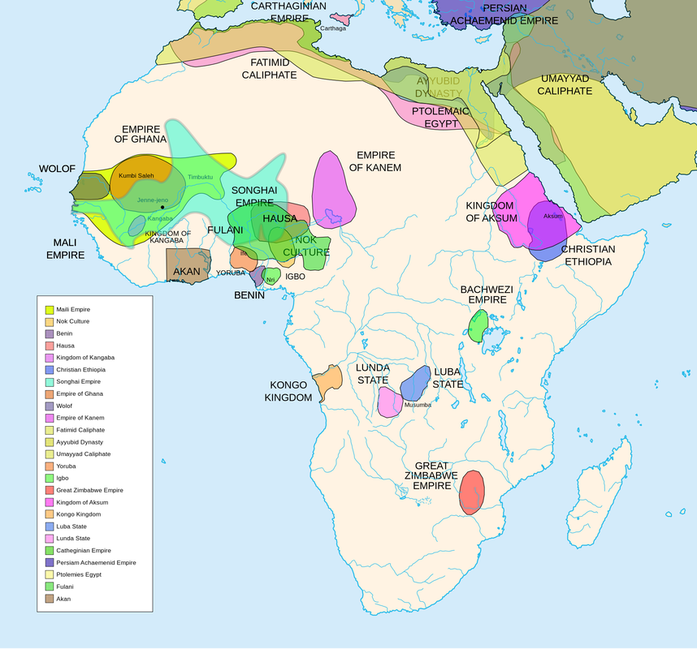
8. Empires in Africa (Ghana, Mali and Songhay) and Asia (Byzantine, Ottoman, Mughal and China) grew as commercial and cultural centers along trade routes.
Resource: West African Kingdoms
Resource: Trekking to Timbuktu: Trade in Ancient West Africa
Resource: A Golden Age: Three West African Empires
Resource: Effects of the Silk Road
- Trade was central to the economic and cultural development of the West African kingdoms of Ghana, Mali and Songhay. Their wealth was primarily from the gold they mined, which attracted traders from Europe and the Middle East. These traders brought goods (e.g., salt, tools, cloth), and introduced Islam to the West African empires. Timbuktu became a leading commercial and cultural setting. It attracted scholars from many places due to its long and rich history of learning in religion, mathematics, music, law and literature.
- Important commercial and cultural centers also developed in Asia. The Byzantine empire flourished when it held the seat of the eastern Roman Empire and continued as an important trade center along the Silk Road. At its height, the Ottoman Empire encompassed much of North Africa, the Middle East and parts of eastern Europe.
- The strong empire of the Mughals in northern India enabled art, architecture and culture to flourish. The Khyber Pass served as an important trade route.
- China’s great commercial and cultural centers grew as a result of its link to the western world through the Silk Road where culture and goods were exchanged.
Resource: West African Kingdoms
Resource: Trekking to Timbuktu: Trade in Ancient West Africa
Resource: A Golden Age: Three West African Empires
Resource: Effects of the Silk Road
Ted-Ed: Mansa Musa, one of the wealthiest people who ever livedView full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/mansa-musa-...
Mansa Musa, the 14th century African king of the Mali Empire, is said to have amassed a fortune that possibly made him one of the wealthiest people who ever lived. Jessica Smith tells the story of how Mansa Musa literally put his empire – and himself – on the map. Lesson by Jessica Smith, animation by Sandro Katamashvili. |
The Mali EmpireThe History of the Empire of Mali For more resources on African History go to: https://www.aelearning.net/
The Empire of GhanaThe Ancient Empire of Ghana For more resources on African History go to: https://www.aelearning.net/
The Songhai EmpireThe History Of The Songhai Empire For more resources on African History go to: https://www.aelearning.net/
|
Trans-Saharan Trade
9. The advent of the trans-Saharan slave trade had profound effects on both West and Central Africa and the receiving societies.
Resource: The Achievements and Challenges of Mali
Resource: History.com - Mansa Moussa: Pilgrimage of Gold
Resource: African Holocaust - African Ledgends
Resource: BU African Studies Center - Primary Source Documents, Cairo 1324 by Mansa Musa, written by Al-Umari
- Slavery existed in Africa long before the arrival of Europeans. Africans became slaves through debt or from being captured in warfare. For centuries, Africans were sold by their rulers to Arab traders who moved them across the Sahara to North Africa to sell in Mediterranean countries. Many Africans died during the transport across the desert.
- Unlike the Atlantic slave trade that began the 16th century, this form of slavery was not race-based. Slaves were more like indentured servants and there was more assimilation of slaves into the culture of North Africa due to the large number of integrated marriages. Slaves generally served as servants or soldiers in contrast to the harsh conditions for slaves in the Americas.
- The trans-Saharan slave trade contributed to the development of powerful African states on the southern fringes of the Sahara and in the East African interior. Rulers who sold slaves grew wealthy. This content serves as a foundational understanding of the slave trade as students will study the trans-Atlantic slave trade in grade eight.
- The trans-Saharan slave trade in Africa contributed to the European rationale for the trans-Atlantic slave trade.
Resource: The Achievements and Challenges of Mali
Resource: History.com - Mansa Moussa: Pilgrimage of Gold
Resource: African Holocaust - African Ledgends
Resource: BU African Studies Center - Primary Source Documents, Cairo 1324 by Mansa Musa, written by Al-Umari
Desert Empires - History Of Africa with Zeinab Badawi [Episode 10]In this episode Zeinab Badawi visits rarely seen historic sites and magnificent ruins in Mali and Mauritania in west Africa. We hear from Africans about how trans-Saharan trade, mainly in gold, meant that by about the 7th century rich kingdoms became established in West Africa. These eventually gave rise to three of the greatest empires on the continent, including the Mali Empire which began in the 13th century. Under armed guard, Zeinab visits the fabled city of Timbuktu, which was overrun by extremists in 2012. Mali’s ruler Mansa Musa was reputedly the wealthiest individual to have ever lived. She brings a rich narrative of a period in Africa’s history when it was a significant player in the world economy, and influenced global thinking through great centres of learning.
Salt Mines of Mali | National GeographicIn the West African desert, gathering and hauling salt is a grueling task not meant for the meek. Camel caravans still move the tablets to market. ➡ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/NatGeoSubscribe
|
Salt: A Brief Big HistorySalt built the Great Wall of China and helped turned New York into America's biggest city. Without it, civilizations would never have thrived and technology would be stuck in the Stone Age. Salt launched wars and sparked revolutions all because humans can't survive without it. Learn more about the Big History series on H2: http://www.history.com/shows/big-hist..., and go even deeper by taking the free, online, Big History Project course: https://www.bighistoryproject.com/bhp....
The Caravans of Gold Workshop Recording
The Caravans of Gold Workshop was a virtual event hosted by the Smithsonian National Museum of African Art on May 28, 2020. This workshop is a collaboration among the Education Department of the Smithsonian National Museum of African Art, Georgetown University’s Center for Contemporary Arab Studies and Center for Muslim-Christian Understanding, and Howard University’s Center for African Studies.
|
The Age of Exploration
10. European economic and cultural influence dramatically increased through explorations, conquests and colonization.
Resource: NEH, EDSITEment - What Was Columbus Thinking?
Resource: The Ages of Explration - The Mariners' Museum and Park
Resource: The Conquistadors
Resource: NEH, EDSITEment - Aztecs Find a Home: The Eagle Has Landed
- As the European powers gained new territories in the Americas, Africa and Asia, they impacted their own economies as well as the areas they claimed. The European powers (e.g., England, France, Portugal, The Netherlands, Spain) gained new wealth from the resources they acquired through their explorations, conquests and colonization.
- The Europeans transformed the cultures of their new territories by establishing similar European governmental structures, converting the indigenous peoples to Christianity, and introducing their languages and technology. They also weakened and supplanted established cultures.
Resource: NEH, EDSITEment - What Was Columbus Thinking?
Resource: The Ages of Explration - The Mariners' Museum and Park
Resource: The Conquistadors
Resource: NEH, EDSITEment - Aztecs Find a Home: The Eagle Has Landed
Resource: All About Explorers *A great resource to teach digital literacy and it may even catch a few unprofessional teachers who do not spend enough time researching their resources!
Description: All About Explorers was developed by a group of teachers as a means of teaching students about the Internet and digital citizenship. Although the Internet can be a tremendous resource for gathering information about a topic, they found that students often did not have the skills to discern useful information from worthless data. All About Explorers has a series of lessons for elementary age students in which they can learn that that just because it is out there for the searching does not mean it is worthwhile.
Description: All About Explorers was developed by a group of teachers as a means of teaching students about the Internet and digital citizenship. Although the Internet can be a tremendous resource for gathering information about a topic, they found that students often did not have the skills to discern useful information from worthless data. All About Explorers has a series of lessons for elementary age students in which they can learn that that just because it is out there for the searching does not mean it is worthwhile.
Ted-Ed: History vs. Christopher Columbus
View full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/history-vs-...
Many people in the United States and Latin America have grown up celebrating the anniversary of Christopher Columbus’s voyage. But was he an intrepid explorer who brought two worlds together or a ruthless exploiter who brought colonialism and slavery? And did he even discover America at all? Alex Gendler puts Columbus on the stand in History vs. Christopher Columbus.
Lesson by Alex Gendler, animation by Brett Underhill.
Many people in the United States and Latin America have grown up celebrating the anniversary of Christopher Columbus’s voyage. But was he an intrepid explorer who brought two worlds together or a ruthless exploiter who brought colonialism and slavery? And did he even discover America at all? Alex Gendler puts Columbus on the stand in History vs. Christopher Columbus.
Lesson by Alex Gendler, animation by Brett Underhill.
Ask History: What Happened to the Aztecs? | HistoryHow and why did the once mighty Aztec Empire crumble in the 16th century? Ask History looks for answers.
Subscribe for more History: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC9MA... Hernan Cortes: Conquered the Aztec Empire - Fast Facts | HistoryAfter establishing a colony in Mexico, Spanish nobleman Hernan Cortes: Fast Facts rallied native allies and conquered the Aztec Empire. Learn more about what led him to destroy one of the greatest civilizations in human history in this video. #Biography
Advanced Students and/or Teacher Readings:
The Broken Spears: The Aztec Account of the Conquest of Mexico
by Miguel Leon-Portilla (Editor), J. Jorge Klor de Alva (Foreword) Fascinating and moving native Aztec descriptions of Cortez's conquest of Mexico. First collected in 1962, now in a new expanded and updated edition. 
The Hummingbird and the Hawk: Conquest and Sovereignty in the Valley of Mexico 1503-1541
by R. C. Padden (Author) A reconstruction of the mythic world of the Aztecs and the changes in Mexico brought about by the arrival of the Spaniards. |
Olmec and Maya Civilizations
The dates for these groups vary greatly depending upon the source, so materials you're studying may not match up. We used dates that were from current materials we trust and we include what some sources call "preclassic" periods as the beginning of civilizations.
Aztecs (Watch and Read version) TURN ON CCWho are the Aztecs? Why do people study them? What are the major accomplishments of the Aztecs? How did social class influence Aztec life? Answers here! The story of the Fifth Sun featuring Nanahuatzin, Tecuciztecatl and Tonatiuh at 9:39
The IncasWhy are the Incas so different from many ideas about empires and civilizations? What does their social hierarchy have in common with other empires and how was it different? How did their empire get so big? Can't get enough potato jokes? All this and more answered!
How we conquered the deadly smallpox virus - Simona ZompiView full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/how-we-conq...
For 10,000 years, humanity suffered from the scourge of smallpox. The virus killed almost a third of its victims within two weeks and left survivors horribly scarred. But Simona Zompi commends the brave souls -- a Buddhist nun, a boy, a cow, a dairymaid and physician Edward Jenner -- who first stopped the spread of this disastrous disease, to make us smallpox-free today. Lesson by Simona Zompi, animation by Augenblick Studios. |
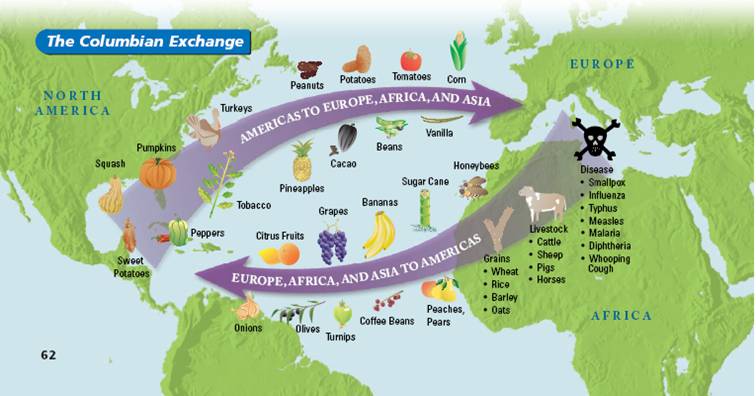
The Columbian Exchange
11. The Columbian Exchange (e.g., the exchange of fauna, flora and pathogens) between previously unconnected parts of the world reshaped societies in ways still evident today.
Resource: The Columbian Exchange
- The Columbian Exchange had a global impact culturally and biologically. The arrival of Columbus in the Americas set in motion the exchange of fauna (animal life), flora (plant life) and pathogens (microorganisms that cause diseases) between Europe, the Americas and the rest of the world.
- Europeans introduced horses, pigs, sheep and cattle to the Americas. Foodstuffs that were transported included bananas, beans, citrus fruits, coffee, grapes, olives, rice and sugar cane. Europeans brought communicable diseases (e.g., measles, small pox) that ravaged the American Indian population.
- American Indians introduced Europeans to turkeys, as well as cacao beans, maize, potatoes, tomatoes, pineapples, pumpkins, peppers and tobacco. Diseases also were carried back to Europe, but with a less devastating impact than those brought to the Americas.
- The cultures in both continents adapted to these exchanges. For example, the horse became central to American Indian life, while the potato became an integral part of the Irish diet.
- The Columbian Exchange impacted societies in ways still evident today. Many countries in the Americas are major producers of foodstuffs and products from animals introduced by the Europeans. Likewise, Europeans are producers and consumers of foodstuffs introduced to them by the American Indians.
Resource: The Columbian Exchange
Geography
Spatial Thinking and Skills
12. Maps and other geographic representations can be used to trace the development of human settlement over time.
Resource: Perry-Castaneda Library: Map Collection
Resource: Location, Location, Location
- Maps and other geographic representations such as aerial photographs, satellite-produced imagery and geographic information systems (GIS) can be used to trace the development of human settlement from the past to the present.
- These tools can be used to show the spatial relationships within and among regions and how these relationships have affected human settlement over time. For example, maps can be used to show trade routes and transportation networks between regions as well as changing political boundaries.
- Maps and other geographic representations can be used to illustrate how population density varies in relation to resources and type of land.
Resource: Perry-Castaneda Library: Map Collection
Resource: Location, Location, Location
The History of the World's Civilizations in 2 Minutes
Geography
Human Systems
13. Geographic factors promote or impede the movement of people, products and ideas.
Lesson: Using Geography to Learn About History
Lesson: Geography Matters in History
- Geographic factors (e.g., climate, bodies of water, mountains, deserts, proximity to natural resources) can contribute to or impede the movement of people, products and ideas. This includes the ability to engage in trade and war, to explore and colonize new lands, to find new places for settlement, and to spread religion and frameworks for governing.
Lesson: Using Geography to Learn About History
Lesson: Geography Matters in History
Culture Heroes: Sarah Parcak | Nat Geo LiveSpace archaeologist and National Geographic Fellow Sarah Parcak uses satellite imagery to track the destruction of cultural heritage sites.
TED: Hunting for Peru's lost civilizations -- with satellites | Sarah ParcakAround the world, hundreds of thousands of lost ancient sites lie buried and hidden from view. Satellite archaeologist Sarah Parcak is determined to find them before looters do. With the 2016 TED Prize, Parcak is building an online citizen-science tool called GlobalXplorer that will train an army of volunteer explorers to find and protect the world's hidden heritage. In this talk, she offers a preview of the first place they'll look: Peru — the home of Machu Picchu, the Nazca lines and other archaeological wonders waiting to be discovered.
|
Archaeology from Space | Sarah Parcak | Talks at GoogleSarah Parcak has one of the most interesting and unique jobs in the world: finding new archaeological sites across the world, using satellite imagery. In her role as the Founding Director of the Laboratory of Global Observation at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, Sarah uses the high-resolution imagery collected by satellites to identify subtle changes to the Earth’s surface, which might signal man-made features hidden underground. In her newest book, "Archaeology from Space," Sarah shows us the evolution, major discoveries, and future potential of the young field of satellite archaeology. From surprise advancements after the declassification of spy photography, to a new map of the mythical Egyptian city of Tanis, she shares her field’s biggest discoveries, revealing why space archaeology is not only exciting, but urgently essential to the preservation of the world’s ancient treasures.
Moderated by: Alex Immerman Get the book: https://goo.gle/2Yld9Lf |
Geography
Trade
14. Trade routes connecting Africa, Europe and Asia fostered the spread of technology and major world religions.
Resource: Trekking to Timbuktu: Trade in Ancient West Africa
Resource: Silk Road: Spreading Ideas and Innovations
Resource: Belief Systems Along the Silk Roads
- Trade routes connecting Africa, Asia and Europe not only provided the exchange of technology, but also helped spread religious ideas.
- The spread of technology took place when caravans from the East brought products such as glass, paper, the magnetic compass and gunpowder along the Silk Road. Caravans from the West brought gold, precious metals and stones, ivory and textiles. Islam expanded as Muslim traders travelled along the Silk Road to Asia and along trade routes connected to African kingdoms. They exchanged goods such as ornamental weapons and utensils.
- Christianity spread into Europe from the Middle East along the trade routes established by the Roman Empire, mainly through the network of roads built by the Romans. It also penetrated China through the Silk Road, the major trade route connecting Europe and Asia.
- Buddhism spread throughout the eastern half of Asia through trade routes that evolved over time, including the Silk Road.
Resource: Trekking to Timbuktu: Trade in Ancient West Africa
Resource: Silk Road: Spreading Ideas and Innovations
Resource: Belief Systems Along the Silk Roads
Silk Road Summit: What is China's 'new Silk Road' project?China says it wants to revive ancient trade routes from Asia to Europe and Africa. But some countries see it as an attempt to promote Chinese influence. TRT World's Azhar Sukri explains
China plans to revive ancient Silk Road trade route stretching from Western Europe to Southeast AsiaChina is planning a transcontinental network of bridges, tunnels, railways and ports that will stretch from Southeast Asia to Western Europe as part of a new Silk Road trade route aimed at creating new markets for Chinese goods.
China calls the proposed trade route the Silk Road Economic Belt, or “One Road, One Belt.” The land-based route will start from the Chinese city of Xi’an and continue through Urumqi in Xinjiang as well as several Central Asian cities before terminating in Venice, Italy. The maritime portion of the Silk Road route begins in Venice, Italy and travels down Africa’s northeastern coast to Mombasa in Kenya. The shipping route continues through the Maldives and a massive Chinese-backed Colombo Port City in Sri Lanka before passing through Southeast Asia and ending in Fuzhou, China. Since Chinese President Xi Jinping entered office in March 2013, he and Premier Li Keqiang have traveled to countries on the historic Silk Road using the planned trade route as a major talking point at official meetings. Capitalizing on increasing internationalization of the renminbi, China has offered low-cost financing to all participating countries so that they can develop the infrastructure necessary for the global venture. Most of the funding for the ambitious plan comes from a $40 billion Silk Road Development Fund and the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank. As China continues to expand its trade network across the world, it has largely ignored the environmental and social impacts of its plans. China’s plans may also do little to appease existing suspicions among many of China’s neighbors who believe China seeks territorial expansion. It is clear that while China believes other countries will also gain from the trade route, China’s ultimate goal is most likely to achieve greater economic, political and cultural influence in countries on the new Silk Road. |
'Silk Road' train from China reaches LondonA train full of Chinese goods has arrived in London after making a trip halfway across the world. This is the first freight train from China's Zhejiang province to Britain and it is hoped it will be the start of a new trade route from China, emulating the ancient Silk Road of more than 2,000 years ago.
New Silk Road - From Yiwu to the WorldIn light of the Belt and Road Forum (BRF), Crossover produced a special episode covering how the Belt and Road Initiative has influenced the economic and cultural life of the people in the city of Yiwu in Zhejiang Province. Xiaojun and Louisa begin their journey at the world-renowned small commodities market, then visit a Senegalese merchant who trades in Yiwu. Next, the hosts make a trip to the legendary straw manufacturer of China who made a global business out of plastic tubes. Finally, Xiaojun and Louisa sit down at the imported commodities mall to discuss the benefits brought and the opportunities opened up by the China Railway Express.
|
Geography
Cultural Diffusion
15. Improvements in transportation, communication and technology have facilitated cultural diffusion among peoples around the world.
- Cultural diffusion refers to the spread of the traits, ideas and products of a culture. Diffusion has increased over time with improvements in transportation, communication and technology.
- Improvements in transportation and technology facilitated cultural diffusion. For example, the roads built by the Romans allowed for the spread of Christianity. The invention of the astrolabe and magnetic compass plus improvements in shipbuilding allowed Spain to explore new lands.
- Improvements in communication and technology facilitated cultural diffusion. For example, the inventions of paper and the printing press both led to mass productions of maps, pamphlets and books. The printing of the Bible hastened the Protestant Reformation.
We explain Cultural diffusion on the silk road.
Created using mysimpleshow – Sign up at http://www.mysimpleshow.com and create your own simpleshow video for free.
Government
Civic Participation and Skills
16. The ability to understand individual and group perspectives is essential to analyzing historic and contemporary issues.
Resource: Cafe Conversations
- Individuals and groups often hold differing perspectives on issues, both historic and contemporary. As students investigate issues, they should be challenged to understand the multiple perspectives that individuals and groups may have.
- For example, to reach an understanding of the dynamics of the trans-Atlantic slave trade, one should analyze the perspectives of those who justified it and those who opposed it, including the slaves. An understanding of the dynamics of colonialism should include an analysis of the perspectives of the colonial power and the colonized.
- It also is essential that one understands what may influence the perspective of an individual or group. These influences can be based on cultural, ethnic, religious or geographical contexts.
Resource: Cafe Conversations
What is Civic Engagement?Civic Engagement happens any time someone takes action to better their community and encourages others to do it, too. Learn more about the basics of Civic Engagement and how you can engage in your community as a civic leader! This film was produced by the Presidential Precinct with support from the University of Virginia's Bicentennial. A special thanks to Next Day Animations. From the birthplace of modern democracy, the Presidential Precinct engages and inspires emerging leaders to address the most pressing challenges in their countries. The Presidential Precinct unites five prestigious institutions, offering leaders the combined academic resources of two of America’s premier public universities: William & Mary and the University of Virginia, and the rich history of three historic sites: James Madison’s Montpelier, James Monroe’s Highland, and Morven Farm.
How To Change The World (a work in progress) | Kid President
In today's adventure, Kid President explores people's different ideas about how to make the world better. What do you think is the best way to change the world?
|
TEDxJacksonville: New models for civic engagement: Ben WarnerDespite our technological advancements, we live in a time where we are increasingly disconnected from one another. Ben Warner believes that, if you don't like it, you should quit talking about it and change it. Join Ben and learn how your community gets to decide what matters most.
Edutopia: Sparking Civic Engagement by Building in Public SpacesSixteen-year-old Alexa gains hands-on experience and leadership skills by collaborating on a play space for kids through Philadelphia's Public Workshop, which promotes community engagement and innovation.. More resources at: http://www.edutopia.org/is-school-eno...
|
Government
Roles and Systems
17. Greek democracy and the Roman Republic were radical departures from monarchy and theocracy, influencing the structure and function of modern democratic governments.
Resource: To Be or Not to Be Democratic
- The Athenian form of democracy invested power with its citizens, not an individual ruler. It was a direct form of democracy since all of the citizens (i.e., males over 18 with Athenian fathers) participated.
- The Roman Republic expanded the Greek model of democracy. It was a representative government with elected officials, division of powers and an emphasis on civic duty. The powers of the Roman government were divided among the Senate, the Consuls and the Assemblies. Roman citizenship was granted to males if they had a parent who was a citizen, was a freed slave or made a huge payment. Citizens had rights and were expected to vote, register for the census and perform military service.
- Many governments today were influenced by the Greek and Roman models. For example, the United States is a representative democracy with a written constitution that limits the powers of the government by dividing them among three branches
Resource: To Be or Not to Be Democratic
Hoover Institute: Friedman - Appropriate Role of Government
|
Ted-Ed: What did democracy really mean in Athens?What did democracy really mean in Athens? - Melissa SchwartzbergView full lesson: ed.ted.com/lessons/what-did-de...
While we might consider elections to be the cornerstone of democracy, the Athenians who coined the term actually employed a lottery system to choose most of their politicians. Melissa Schwartzberg describes the ins and outs of the Athenian democracy, and addresses some ways in which a lottery system might benefit us today. Lesson by Melissa Schwartzberg, animation by TED-Ed. |
Nation States
18. With the decline of feudalism, consolidation of power resulted in the emergence of nation states.
Resource: NEH, EDSITEment - Magna Carta: Cornerstone of the U.S. Constitution
- There were many causes of the decline of feudalism in Western Europe, including the impact of trade that developed as a result of the Crusades, the transition from a land-based economy to a money-based economy, the growth of towns and the increase in centralized governments.
- Kings began to consolidate power, lessening the power of nobles. This led to the rise of nation states (i.e. sovereign territorial units characterized with defined borders, common languages, culture and values).
- As England emerged as a nation state, the lesser nobles limited the authority of the king by forcing him to sign the Magna Carta. The document placed limits on the power of the king and led to the development of democratic principles that influenced the Declaration of Independence and American Revolution.
Resource: NEH, EDSITEment - Magna Carta: Cornerstone of the U.S. Constitution
The Story of Magna CartaWhy did King John seal Magna Carta at Runnymede in June 1215? And what happened next?
This animated film tells the history of Magna Carta and explains how it has become a global symbol for Human Rights. Created by the Guy Fox Team as part of the 'Happy Anniversary, Magna Carta!' project, which was funded by the Heritage Lottery Fund and supported by an army of volunteers. |
What is Magna Carta?Why is this old piece of parchment considered to be such a powerful symbol of our rights and freedoms? Narrated by Monty Python’s Terry Jones, this animation takes you back to medieval times, when England under the reign of Bad King John. It asks why Magna Carta was originally created and what it meant to those living in the 13th century.
Find out more about Magna Carta at the British Library’s website – http://www.bl.uk/magna-carta |
Economics
Decision Making and Skills
19. Individuals, governments and businesses must analyze costs and benefits when making economic decisions. A cost-benefit analysis consists of determining the potential costs and benefits of an action and then balancing the costs against the benefits.
- Economic decisions, whether they are made by individuals, governments or businesses, are generally made by weighing the costs with the benefits. The desired choice is when the benefits of a decision exceed the costs. This decision-making process is referred to as cost-benefit analysis.
- For example, individuals weigh the potential costs and benefits of purchasing expensive products or attending college. Governments do the same when making economic decisions such as erecting public buildings or funding military actions. Historical examples can be found in decisions of early civilizations and countries to establish trade routes, engage in slave trade, explore and colonize new lands. Businesses determine the potential costs and benefits of activities such as investing in research and development, expanding or changing production.
TED Ed: The psychology behind irrational decisions - Sara Garofalo
View full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-psychol...
Often people make decisions that are not “rational” from a purely economical point of view — meaning that they don’t necessarily lead to the best result. Why is that? Are we just bad at dealing with numbers and odds? Or is there a psychological mechanism behind it? Sara Garofalo explains heuristics, problem-solving approaches based on previous experience and intuition rather than analysis.
Lesson by Sara Garofalo, animation by TOGETHER.
Often people make decisions that are not “rational” from a purely economical point of view — meaning that they don’t necessarily lead to the best result. Why is that? Are we just bad at dealing with numbers and odds? Or is there a psychological mechanism behind it? Sara Garofalo explains heuristics, problem-solving approaches based on previous experience and intuition rather than analysis.
Lesson by Sara Garofalo, animation by TOGETHER.
Economics
Scarcity
20. The variability in the distribution of productive resources in the various regions of the world contributed to specialization, trade and interdependence.
Resource: Effects of the Silk Road
- Productive resources are not distributed equally around the world. Productive resources (i.e., natural resources, human resources and capital goods) are the resources used to make goods and services. The abundance or lack of resources in a region contributes to specialization and trade with other regions.
- Specialization is the concentration of production on fewer kinds of goods and services than are consumed. When regions and/or countries specialize, they trade to obtain goods and services they want but do not or cannot produce. As societies grew and trade expanded, interdependence increased.
- For example, the availability of productive resources such as tea and spices in Asia, tobacco, cotton, coffee, gold and silver in the Americas, and ivory and gold in Africa, led these regions to specialize. They traded for goods they did not have and wanted. This exchange promoted global interdependence.
Resource: Effects of the Silk Road
TED-Ed: Fresh water scarcity: An introduction to the problem - Christiana Z. Peppard
View full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/fresh-water... Fresh water is essential for life -- and there's not nearly enough of it for the world right now. Why is that, and what could we do? Christiana Z. Peppard lays out the big questions of our global water problem. And no, shorter showers are not the answer. Lesson by Christiana Z. Peppard, animation by Jeremy Collins.
Economics
Markets
21. The growth of cities and empires fostered the growth of markets. Market exchanges encouraged specialization and the transition from barter to monetary economies.
- Markets grew with the development of cities and empires. The increased demand of goods and services by larger populations led to the growth of markets.
- Consequently, growth of markets encouraged specialization and advanced a more efficient system for the exchanges of goods and services. The barter system limited market exchanges, so money-based systems were created.
TED-Ed: How does the stock market work? - Oliver Elfenbaum
Download a free audiobook version of "The Richest Man in Babylon" and support TED-Ed's nonprofit mission: https://www.audible.com/ted-ed Check out our full book recommendation: https://shop.ed.ted.com/products/the-... -- In the 1600s, the Dutch East India Company employed hundreds of ships to trade goods around the globe. In order to fund their voyages, the company turned to private citizens to invest money to support trips in exchange for a share of the profits. In doing so, they unknowingly invented the world’s first stock market. So how do companies and investors use the market today? Oliver Elfenbaum explains. Lesson by Oliver Elfenbaum, directed by Tom Gran & Madeleine Grossi.